Handicap 3
A golf handicap is the game's great equalizer.
With a certified handicap you have a fair chance to win a net score match against a superior player. The first step to acquiring an official handicap under the United State Golf Association system is to establish a handicap index. You must establish your index at a club that’s certified to use the USGA’s handicap system.
Index
The handicap index is 'a measurement of a player's potential ability on a course of standard playing difficulty,' according to the USGA. The golfer uses the handicap index to determine his handicap at a particular course, based on the difficulty of that course.
- Each full stone of handicap on a 13×13 board is in any case probably equivalent to about 2.5 to 3 ranks, and each full stone on a 9×9 board is equivalent to about 6 ranks. For example, if the appropriate handicap is 9 (i.e., 8.5) stones on a 19×19 board, the handicap between those two players is reduced to 4 (because 3.5 × 2.5 = 8.75.
- Lots of betting sites from all over the world offer bettors 3-Way Handicap bets, alongside European and Asian handicap bets. There isn’t a significant difference between these three styles. 3-Way Handicap bets focus on the same three outcomes as outright bets: home team to win, draw, or away team to win.
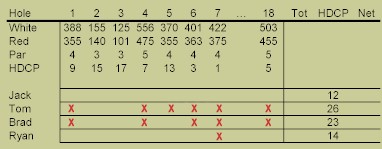
Meaning 3 handicapper would average almost 4 strokes over the rated par — or about 72. People use handicaps to make golf games a little more fair between people of different skill levels. A 6 handicapper playing a 3 handicapper would get a three- stroke adjustment in.
The golfer can receive a handicap index after posting five scores, but the handicap will eventually be based on 20 rounds.
Because a handicap is designed to measure a player’s peak ability, rather than his average play, his index is calculated by using the 10 best of his 20 most recent scores. The handicap service to which the club subscribes -- such as the USGA's GHIN service or GolfNet -- calculates the golfer's handicap index using a complex formula.
The maximum handicap index is 36.4 for a man, 40.4 for a woman. Handicap indexes are typically updated every two weeks.
Course Ratings
A player’s handicap index can be adapted to any course that has a USGA rating. Courses are rated in two ways. The course rating indicates the typical number of strokes a scratch golfer – generally meaning a zero handicap player – will take under normal conditions. Typically, courses have ratings from the high 60s to the middle 70s.

The course’s slope rating measures a course’s difficulty relative to a “bogey player” -- someone who will carry a course handicap of 20 on a course of standard difficulty.
The lowest possible slope rating, which is given to the easiest courses, is 55, while the highest is 155.
A course of average difficulty carries a slope rating of 113. For example, California's famed Pebble Beach Golf Links has a course rating of 75.5 and a slope rating of 145 from the back tees.
Course Handicap
A handicap index is translated into a course handicap by employing another USGA formula.
To make it easy, clubs generally post a chart – based on the course’s slope rating – that translates a player’s handicap index into her actual handicap for that particular course. The USGA also provides an online course handicap calculator.
Handicap Index Translated
If a golfer with a handicap index of 10.0 plays a course with a slope rating of 100, his course handicap is 9. The handicap goes down because the course is slightly easier than average.
If the same golfer plays a course rated 125, however, his course handicap rises to 11. The course handicap is always expressed as a whole number.
Within most systems and at most levels in the game of Go, a handicap is given to offset the strength difference between players of different ranks.
Forms of handicaps[edit]
In the game of Go, a handicap is given by means of stones and compensation points. In contrast to an even game, in which Black plays first, White plays the first move in a game with handicap (after Black's handicap stones have been placed).
Handicap stones[edit]
The rank difference within a given amateur ranking system is one guide to how many handicap stones should be given to make the game a more equal contest. As a general rule, each rank represents the value of one stone. (In terms of points, one stone is considered to be 13-16 points, but this figure is not constant over levels: the more skillful a player, the greater the usefulness of each stone.)
For example, a 3 kyu player gives a 7 kyu player four handicap stones to allow for an interesting game with roughly equal challenge for both players. If traditional fixed placement of the handicap stones is used, nine stones is normally the maximum handicap. Larger handicaps are certainly possible; but with such a great difference in strength, Black may be simply bewildered, and not understand how many of White's moves relate to his own.
The above rank relationship reliably applies for single-digit kyu (1-9k) and amateur dan (1-7d) ranks. The advantage of moving first is equivalent to only half a stone of handicap, as the opponent then has the initiative. Because White gets the next move after Black places the handicap stones, a nominal handicap of n stones is therefore in reality half a stone less than n.
Nowadays professional ranks are awarded by professional Go players' organizations; they are, unlike amateur ranks, not reliable as a measure of current playing strength, but rather an indication of achievements. Before the late 20th century, they were used as strength measurement, with a difference in skill of less than a third of a stone per rank.
Small board handicaps[edit]
Small boards are often used for novice players (double-digit kyu players) just learning to play Go, or for quick games. As the fewer moves made when playing on smaller boards gives White fewer chances to overcome the advantage conferred by the handicap, smaller handicaps are used on smaller go boards (most commonly 13×13 and 9×9).[1]
The per-rank handicap is therefore reduced, by a scaling factor. Various estimates have been given for the factor that applies to 13×13, in the range 2.5 up to 4; and on grounds both theoretical and experimental (small-board tournament play). The evidence is that 2.5 is more realistic than 4, for clock games. The corresponding factor for a 9×9 board is not easy to understand, and the change for each stone added is very large.
One theoretical approach is according to the distribution of the number of moves made in a game on a board of a given size relative to the number made on a 19×19 board. Using estimates that a 19×19 game will last about 250-300 moves, a 13×13 game about 95-120 moves, and a 9×9 game about 40-50 moves, a quadratic formula for the ratio of the mean number of plays may apply. Arguing that White catches up by means of Black's 'small errors', so that White's deficit drifts at a constant rate, it makes sense to take the ratio of game lengths as scaling factor.[2]
Each full stone of handicap on a 13×13 board is in any case probably equivalent to about 2.5 to 3 ranks, and each full stone on a 9×9 board is equivalent to about 6 ranks. For example, if the appropriate handicap is 9 (i.e., 8.5) stones on a 19×19 board, the handicap between those two players is reduced to 4 (because 3.5 × 2.5 = 8.75) stones on a 13x13 board and 2 (1.5 × 6 = 9) stones on a 9×9 board. A 5 (i.e., 4.5) stone handicap on a 9×9 board is accordingly equivalent to a handicap of 27 or 28 stones on a 19×19 board.
These figures are not a consensus, but have wide support. They can be used to give rankings, by converting 13×13 handicaps back to rank difference.
Handicap placement[edit]
Fixed placement[edit]
There are 9 star points marked on a 19 x 19 board – in each corner on the (4,4) point, in the middle of each side on the fourth line, (4,10); and the very center of the board, (10,10). Traditionally handicaps are always placed on the star points, as follows:
| Stones | Placement | Locations |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Black plays his first stone as he wishes, and gives no komi | None |
| 2 | Black plays the star points to his upper right and lower left | A,B |
| 3 | Black adds the star point to his lower right (In Classical Chinese rules the third handicap stone is place on tengen) | A,B,C (or E) |
| 4 | Black takes all four corner star points | A,B,C,D |
| 5 | Black adds the center star point | A,B,C,D,E |
| 6 | Black takes all three star points at left and right | A,B,C,D,F,G |
| 7 | Black adds the center star point | A,B,C,D,E,F,G |
| 8 | Black takes all star points except the center | A,B,C,D,F,G,H,I |
| 9 | Black takes all nine star points | A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H,I |
As the stones are always at the same (4,4) points in the corners, Black always plays more (4,4) openings, and doesn't gain experience playing the (3,4) openings, or others such as (3,3), (5,4), (5,3), etc., except on two and three stones.[3]
Free placement[edit]

Recently, some have advocated free placement of handicap stones. Free placement means one can place handicap stones anywhere on the board without restriction. Here is the list of countries[4] and servers[5] that use free placement of handicap stones:[6]
| Fixed Placement | Japan, Korea, United States (by default), IGS online server |
|---|---|
| Free Placement | Chinese, Ing, New Zealand |
Although free placement is less common because many players are attached to tradition, especially in East Asian countries, it offers advantages which are not available with fixed placement.
Advantages[edit]
For weaker players:
Handicap 3 Wheel Bicycle
- They can choose their opening strategies according to their own understanding of the game, and thus follow a consistent strategy.
- They can think for themselves and learn about different opening strategies through actual game experience.
- The mandatory handicap points stress influence rather than taking territory directly; some weaker players have a more territorial style.
- They can learn a much larger range of corner plays in actual competition against stronger opponents.
For stronger players:
- Many more variations with fewer repetitions mean the game is more refreshing, challenging, and interesting to the strong player. They may be more willing to play and teach the weaker player.
Disadvantages[edit]
With free placement, weaker players may not place their stones in respect to their comparable handicap to their opponent, thus eliminating the point of the handicap. The standard fixed handicap points allow for a good standard that allows novices to have the handicap they need since they are not experienced and may not be able to take advantage of the free placement of handicap stones. Therefore, free placement handicap may be best suited for more experienced players or those who want more flexibility and variety in play.
Compensation points[edit]
When the difference in strength is one rank, no handicap stone is given. Instead the stronger player takes White but without compensation points. The compensation points are called Komi in Japanese. It is a custom that Black plays first; White moves second. Playing first is regarded as a significant advantage in modern go, and to make the game fair to both players, this advantage must be compensated. It is regarded that playing first is equal to half a move or more ahead throughout the game.
Another common type of compensation used is the reverse compensation points, where the weaker player takes black, and is given both the first move and compensation points too. This is more advantageous than the above situation.
Compensation points are sometimes preferred to stones because the players would like to play or practice as if it is an even game. They would like to have the feel of an 'even game'. White (the stronger player) must play better to overcome these disadvantages (points gained by playing first + compensation points).
Fixed compensation point (Komi) system[edit]
When ranks are equal, Black gets advantages by playing first. The advantage of that first move is compensated by compensation points. However, there are still no absolute standards on the number of compensation points due to the difficulty of determining a fair value. 6.5 points are used in Japan and Korea. 7.5 points are used in China and America (see AGA rules). The 0.5 points is used to prevent a draw.
Auction compensation point system[edit]
As no one can be absolutely sure what the fair number of compensation points is, some advocate another system which is often used in some amateur matches and tournaments. There are no fixed compensation points. The decision is left to both players. They arrive at a value through negotiation and bidding. This is called auction compensation point system.
Examples of auction komi systems include:
Handicap 3 Way Soccer
- one player chooses how big komi will be given to White and the other player then chooses to play Black or White.
- the game is without komi; one player makes the first move of Black (not too weak and not too strong) and the other one then chooses to play Black or White. This is an application of the pie rule.
- the players do an 'auction' by saying: 'I am willing to play Black against XXX komi' and the player who wins the auction plays Black.

Handicap strategy[edit]
Handicap go is the traditional form of teaching given to go players. Fixed handicap placements are in effect a form of graded tutorials: if you cannot beat your teacher with a nine-stone handicap, some fundamental points are still to be learned.
Handicap 3.5 Meaning
The pedagogic value of fixed handicaps is an old debate for Western players. The 'theory' of handicap go shares with much of the rest of the Japanese pedagogic go literature a less explicit approach, based on perception as much as analysis. Whether fixed handicap placement makes it easier or more difficult for the weaker player to learn these fundamental points is moot. The nature of these 'tutorial' steps may certainly be misunderstood and contested by Western players new to the game. Handicaps are also unpopular with Chinese players, who have more of a tradition of equality at the board rather than deference to a teacher.
There are some book treatments of low-handicap go by strong professionals (Kobayashi Koichi and Kajiwara Takeo, in particular); and examples of pro-pro games to follow. With the traditional handicap placements, the only consistent strategy Black can follow depends on the use of influence. This is particularly true in the early stages of the middle-game fighting.[7]
While Black often assumes that consolidating territory from the opening stages should be enough to win, that is not the case when the handicap stones are placed on the star points, where they are more effective in obtaining influence than territory. If Black does not understand and utilize the value of star-point handicap stones for attack, White will gradually build a more advantageous position, and steadily close the gap.
Notes and references[edit]
- ^See page at Sensei's Library for a fuller discussion
- ^Psychologically speaking, Black (the pupil) probably sees blunders as more important in a loss; but White (the teacher) is more aware of getting into the game by means of Black's inefficiencies.
- ^Historically, in China, Black and White were constrained to play on diagonally-opposite star points for their first two moves in even games. In Japan, from some point in the sixteenth century perhaps, the board was empty in even games. The consequence was a deeper study of the joseki that in the Chinese system were used only in three-stone handicaps. Those joseki dominated opening theory in Japan, until the shinfuseki period of the 1930s. In contemporary go, the 4-4 point openings are fundamental.
- ^Handicap placement convention and effect actually depends on different rule sets, such as Japanese or Chinese rules, and not on different countries. Not all countries have their own rule sets
- ^Some servers offer a choice between different rule sets
- ^Comparison of some Go rules
- ^See for example the book Kage's Secret Chronicles. In it more explicit reference is made, than is typical, to the need to fight hard rather than play slackly, in order to use the handicap stones properly. This lesson on influence is at the heart of the traditional system.